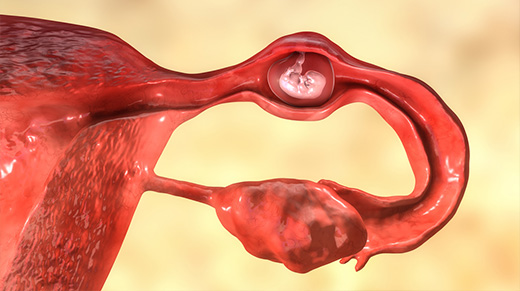
You will learn about ectopic pregnancies on this page and the safest methods for managing them.
One potentially fatal side effect of pregnancy is ectopic pregnancy. It happens in 2 to 5 occurrences out of every 1,000 pregnancies and occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
Older age, heavy menstrual cycles, obesity, having several sexual partners, and being underweight raise the chance of ectopic pregnancy.
Women who have experienced one ectopic pregnancy may be more likely to do so again.
The following are the most typical symptoms of ectopic pregnancy; if you experience any, you should consult your doctor first:
- Pain in the pelvis, lower abdomen, or area below the belly button.
- Bleeding from the cervix, typically a brownish discharge.
- Nausea, discomfort, abdominal swelling, and vomiting
The first few weeks are when these symptoms are most prevalent. Blood clots typically form in the fallopian tubes after two to three months. Compared to a typical intrauterine pregnancy, your odds of delivering the baby to term are much reduced. The most hazardous consequence following an ectopic pregnancy is shock and a higher chance of infertility.
Some of the common treatments for ectopic pregnancy are:
- Medications: A typical pregnancy’s medical care is comparable to an ectopic pregnancy. Antibiotics are frequently administered because they can reduce the risk of miscarriage. Progesterone supplements and pelvic rest are effective treatments for women who haven’t previously experienced an ectopic pregnancy. Mifepristone, a medication that aids in the fallopian tube’s emptying, is occasionally paired with pelvic rest.
- Surgery: Another solution is to have a laparoscopic procedure. A tiny tube known as a cannula is inserted into the stomach to access the cervix during the procedure. The ectopic pregnancy can be removed in a less harmful and painful manner.
- Tubal ligation or salpingectomy: A tubal ligation is the last available alternative. A surgeon will cut open the fallopian tube and remove the embryo from the uterus. Although it’s doubtful that you’ll become pregnant following this operation, there might be major problems if you do.
Conclusion
Although it can happen to anybody, ectopic pregnancies most frequently affect women between the ages of 15 and 24. If this ailment is not addressed immediately, it might be hazardous. If the developing embryo is not attended to, it may burst, resulting in excessive bleeding, sterility, and other problems. To avoid serious consequences from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, you should visit your gynecologist expert in Indore as soon as possible if you have an ectopic pregnancy.